Chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam, a remarkable material with a fascinating history and a wide array of applications, has a story waiting to be unveiled. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a versatile solution in various industries, this foam has undergone a remarkable journey of evolution and innovation.
Initially discovered as a byproduct of research in the mid-20th century, chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam has come a long way from its accidental creation. Through years of development and refinement, this material has transformed into a crucial component in modern manufacturing processes, offering unique properties that set it apart from conventional materials.
Delving into the manufacturing process of chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam reveals a complex and intricate procedure that requires precision and expertise. By utilizing advanced methods and cutting-edge technologies, manufacturers are able to create a durable and resilient material that can withstand various environmental conditions and mechanical stresses.
You can review the following pages of Durfoam:
The key properties of chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam, including its exceptional durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals, make it a sought-after choice in industries such as packaging, insulation, and automotive. Its ability to provide cushioning, insulation, and protection in a lightweight and cost-effective manner has led to its widespread adoption across diverse applications.
History and Development
Chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam has a fascinating history that dates back to its initial discovery in the mid-20th century. Originally developed as a material with unique properties, it quickly gained recognition for its versatility and durability. Over the years, advancements in manufacturing techniques have further enhanced the quality and applications of this remarkable foam.
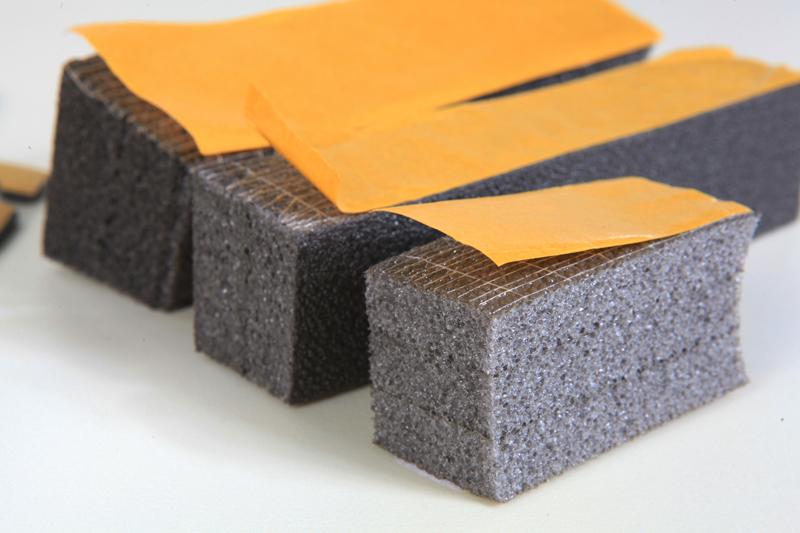

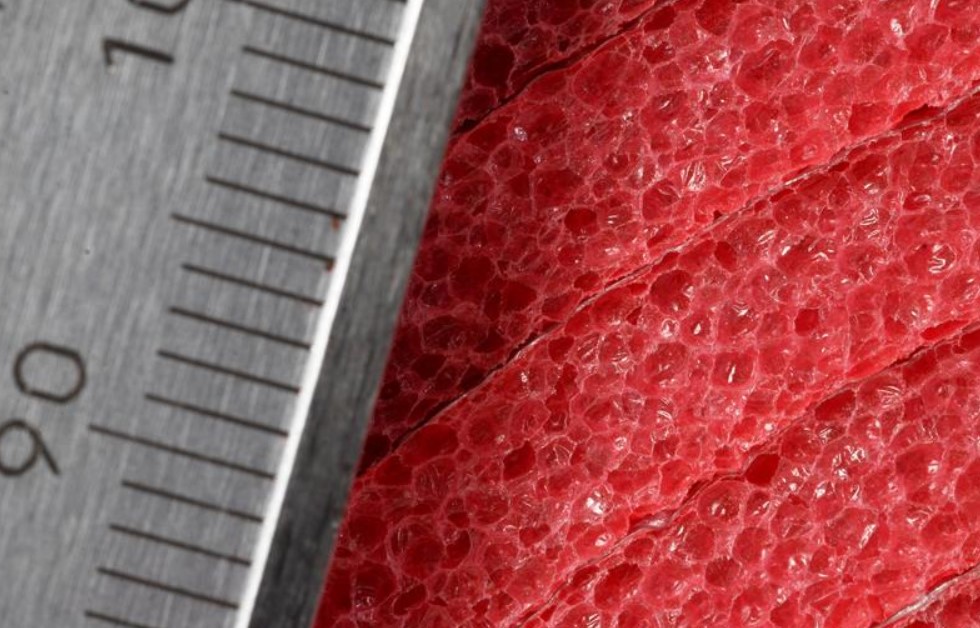
During its development, chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam underwent significant transformations to meet the evolving needs of various industries. The process of cross-linking involves creating strong molecular bonds within the polyethylene structure, resulting in a material that is resilient, lightweight, and resistant to wear and tear.
The evolution of chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam can be likened to a journey of discovery and innovation. As researchers delved deeper into its potential, they unlocked new ways to enhance its properties and broaden its applications. This journey of development has paved the way for the foam to become a staple material in diverse industries.
Through meticulous research and experimentation, manufacturers have refined the production process of chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam. By utilizing cutting-edge technologies and precise techniques, they have been able to create foam products that meet stringent quality standards and exceed performance expectations.
Today, the legacy of chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam continues to grow as it finds its place in a wide range of applications. From cushioning and insulation in packaging to impact absorption in automotive components, the foam’s history and development have laid the foundation for its widespread use across industries.
Manufacturing Process
When it comes to the manufacturing process of chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam, it involves a series of intricate steps that result in the creation of a durable and versatile material. The process begins with the selection of high-quality polyethylene resin, which serves as the foundation for the foam’s structure.

Next, the resin is mixed with specific additives and cross-linking agents to enhance its properties and promote the cross-linking reaction. This reaction is crucial as it forms a three-dimensional network within the foam, increasing its strength and durability.
During the manufacturing process, the resin mixture is subjected to heat and pressure in a controlled environment. This combination of heat and pressure triggers the cross-linking process, allowing the foam to expand and take on its characteristic cellular structure.
Once the foam has been formed, it undergoes a curing process to ensure the cross-linking is complete and the material achieves its desired properties. This curing stage may involve cooling the foam gradually to stabilize its structure and enhance its overall performance.
Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control measures are implemented to monitor the foam’s density, cell structure, and overall consistency. These checks help ensure that the final product meets the required specifications and maintains its integrity for various applications.
Properties and Applications
Chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam boasts a myriad of properties that set it apart as a versatile material suitable for a wide range of applications. One of its key characteristics is its exceptional durability, providing long-lasting performance even in demanding environments. This durability is further enhanced by the material’s resistance to chemicals, making it a reliable choice for applications where exposure to various substances is a concern.
Another standout feature of chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam is its flexibility, allowing it to conform to different shapes and contours with ease. This flexibility makes it an ideal option for packaging solutions where cushioning and protection are paramount. Additionally, the material’s lightweight nature adds to its appeal, offering a balance of strength and ease of handling.
When it comes to applications, chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam finds extensive use in the packaging industry. Its cushioning properties make it an excellent choice for protecting fragile items during shipping and handling. The material’s ability to absorb impact energy helps prevent damage, ensuring that products reach their destination intact.
In the realm of insulation, chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam excels at providing thermal and acoustic insulation. Its closed-cell structure traps air, creating a barrier that helps regulate temperature and reduce sound transmission. This makes it a popular choice for applications where maintaining consistent temperatures and minimizing noise are crucial.
Moreover, the automotive industry benefits greatly from the properties of chemically cross-linked polyethylene foam. From gaskets and seals to interior components and underbody protection, the material’s durability and resistance to chemicals make it a reliable choice for various automotive applications. Its lightweight nature also contributes to fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.